Hi, how are you doing?
Are you looking at having a fantastic career in tech? You can not avoid the use of git and of course, storing files on GitHub or any version control platform tho I prefer GitHub. This can be overwhelming at first, it is a simple walkover with access to the correct manuals and documentation like this article to help you out. We'll try to examine how Git is essential to the life of a software developer through this article and understand the fundamentals of the GitHub workflow.
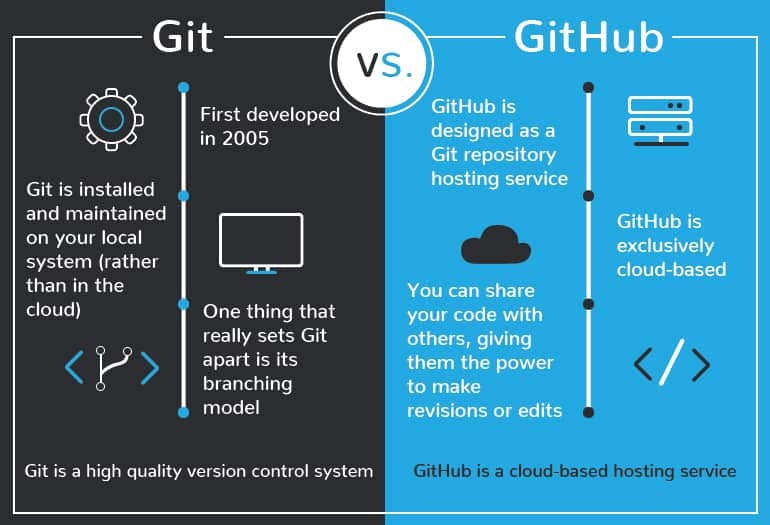
What is Git and Github?
Linus Torvalds, the man behind the Linux Kernel, created Git in 2005. Git is a distributed version control system for tracking changes in source code during software development. It is designed for coordinating work among programmers, but it can be used to track changes in any set of files. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows.
GitHub on the other hand is a web-based hosting service for Git repositories. It offers collaboration functionality like project management, support ticket management, and bug tracking. With GitHub, developers can share their repositories, access other developers’ repositories, and store remote copies of repositories to serve as backups. GitHub is a social platform for hosting code and files that work with Git. When multiple people collaborate on a project, it’s hard to keep track of revisions — who changed what, when, and where those files are stored. GitHub takes care of this problem by keeping track of all the changes that have been pushed to the repository.

Pair programming will be a big part of your job as a software developer, whether it's for business, hackathons, or any other project in general. A version control system such as Git is required to maintain and manage your codebase and prevent any conflicts between your code. You may perform the same thing using the remote repositories offered by GitHub.
Difference between Git and Github
Create a Github Account
Visit the GitHub website and create a GitHub account. If you're a student, consider getting a GitHub Student Developer Pack which provides you with different tools and resources to start your tech journey.
Note: The GitHub account details (your email address and display name) will be needed to configure Git.
How to Install and Configure Git
- Download and install git from Git website
 Up there is a quick guide to install git - NOTE: It will be different based on your operating system.
Run the installer and set up git on your computer.
Up there is a quick guide to install git - NOTE: It will be different based on your operating system.
Run the installer and set up git on your computer.
- Next, run the following command in your command-line interface to check if you have successfully installed Git.
git --version
It should show you a version of Git (something like git version 2.36.1), otherwise, drop a comment with a screenshot so you can be helped with the installation process.
Recommended: Watch this installation guide by Codemy School
Git Workflow explained
Before diving in, there are some basic terms you need to understand. These are;
- Repositories: File location where all your code is stored
- Commit: An individual change to a file
- Branch: A lightweight movable pointer to a commit
- Clone: A local version of a repository, including all commits and branches
- Remote: A common repository on GitHub that all team members use to exchange their changes
- Fork: A copy of a repository on GitHub owned by a different user
- Pull request: A place to compare and discuss the differences introduced on a branch with reviews, comments, integrated tests, and more
- Head: Representing your current working directory, the HEAD pointer can be moved to different branches, tags, or commits when using git checkout.
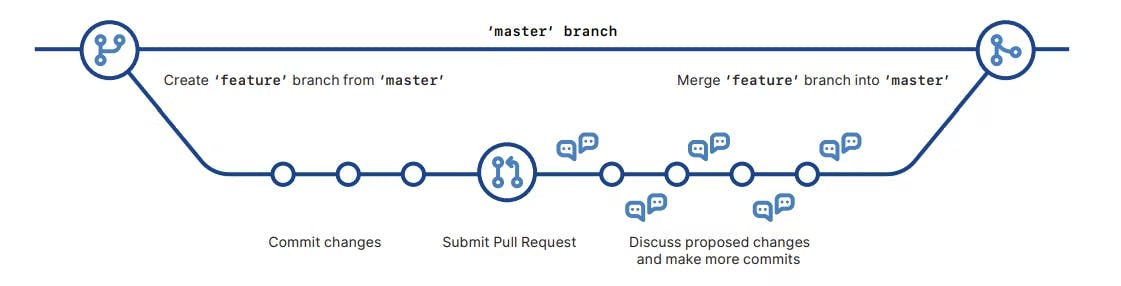 Image: Git Flow Diagram - View the GitHub Cheatsheet to learn more
Image: Git Flow Diagram - View the GitHub Cheatsheet to learn more
We are looking at a GitHub flow graphically, as can be seen above. To save your work without changing the master branch, you must create branches using a branch-based workflow.
This makes it easier for other team members to discuss, provide answers to queries, and make code suggestions while also allowing them to review your code through pull requests.
Some Basic Linux Commands.
- ls: This command is used to list files or directories.
- cd: Stands for change directory it can go inside a directory by using.
- cd ..: It is used to come outside the folder you're into.
- touch: It will create a new file.
- vim: It will help you make changes in files using your terminal.
- cat: The most commonly known usage is to print the content of a file onto the standard output stream.
Other git commands you should know.
- git status lets you know the changes that are tracked and those that are not.
- git log displays the history of commits on your local repository.
- git clone downloads a copy of a remote repository to your machine.
- git pull pulls the latest update from a remote repository to the local version on your machine.
- git branch lets you create or delete a branch
Sample Git commands used

Conclusion
As a developer, you'll use Git and Github as tools. Although they could be challenging to learn on your first attempt, with persistent practice, you will become proficient with these tools.
Subscribe and follow to get notified of the next post - Learn Git and Github - the Beginner's Guide (Part Two)
Feel free to ask any questions in the comment box below if you have.
